Trauma in early childhood can be especially harmful. Early childhood trauma generally means trauma between birth and the age of six. A child’s brain grows and develops rapidly, especially in the first three years. Young children are also very dependent on caregivers for care, nurture, and protection. This can make young children especially vulnerable to trauma. When trauma occurs early it can affect a child’s development. It can also affect their ability to attach securely, especially when their trauma occurs with a caregiver.
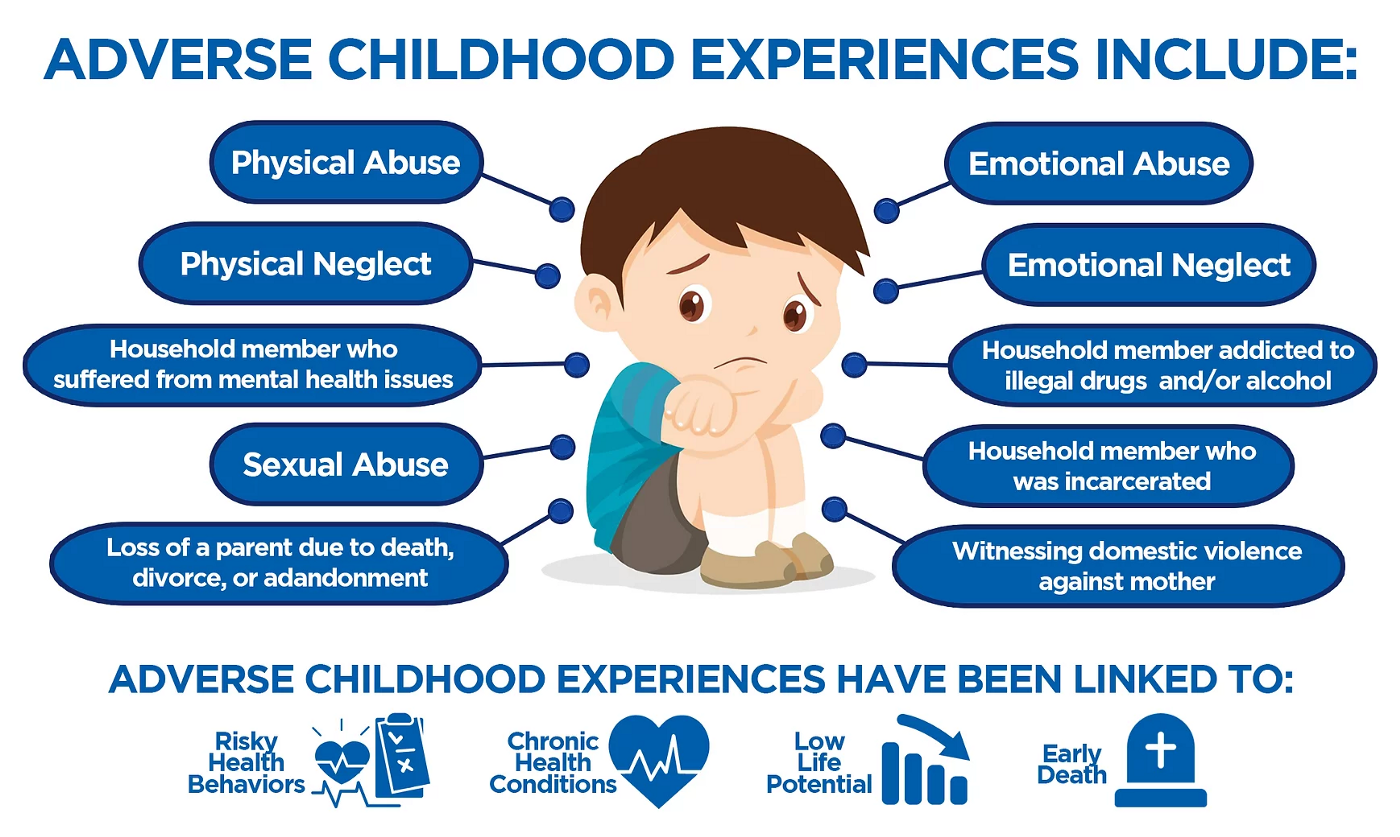
Examples of childhood trauma include:
Physical abuse
Sexual abuse
Psychological and emotional abuse
Neglected Trauma
Natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or fires
Homelessness
Racism
Serious accidents or life-threatening illness
Violent loss of a loved one
Sexual exploitation
Refugee and war experiences
Community and school violence
Witnessing or experiencing family or partner violence
Unexplained traumas

“The experience of an event by a child that is emotionally painful or distressful, which often results in lasting mental and physical effects.”
Childhood trauma can occur when a child witnesses or experiences overwhelming negative events in childhood. Many childhood experiences can overwhelm a child. These can occur in relationships such as with abuse, assault, neglect, violence, exploitation or bullying. This is known as interpersonal trauma – trauma that happens between people.

